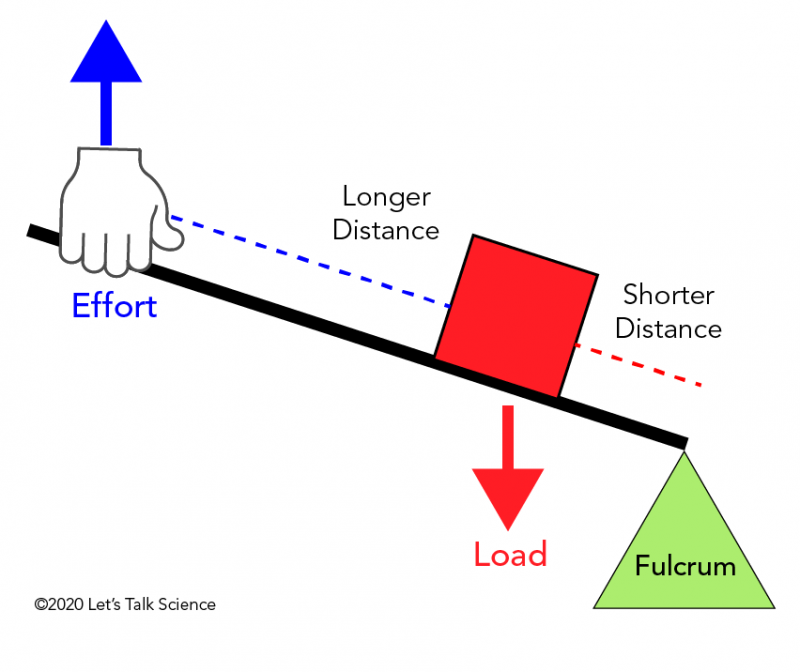
How Leverage Works Physics . The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. This browser doesn't support html5. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. You cannot pull any out of thin. The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. A lever is a force. Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs.
from letstalkscience.ca
Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. A lever is a force. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. This browser doesn't support html5. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces.
Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science
How Leverage Works Physics A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. You cannot pull any out of thin. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. A lever is a force. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. This browser doesn't support html5. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance.
From www.vecteezy.com
Levers simple machine science experiment poster 3274742 Vector Art at How Leverage Works Physics This browser doesn't support html5. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. A lever is a force. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. Web d2n2 −d1n1 =. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.youtube.com
What is Leverage Explained in 2 min YouTube How Leverage Works Physics Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. Web in physics, work is defined as force. How Leverage Works Physics.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Leverage Works Physics The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. This browser doesn't support html5. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. A lever is a force. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam.. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.janereactionfitness.com
Physics of Fitness Fridays Body Levers — Jane Reaction Fitness How Leverage Works Physics Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. This browser doesn't support html5. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. The relative positions of. How Leverage Works Physics.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Leverage Works Physics Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. A force is applied somewhere on. How Leverage Works Physics.
From vhmsscience.weebly.com
Levers & Mechanical Advantage VISTA HEIGHTS 8TH GRADE SCIENCE How Leverage Works Physics Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. You cannot pull any out of thin. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.youtube.com
Principle of Lever Mechanics YouTube How Leverage Works Physics The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. A lever is a force. The beam pivots around the fulcrum. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT SIMPLE MACHINESPRINCIPLE OF LEVERAGE PowerPoint Presentation How Leverage Works Physics Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to. How Leverage Works Physics.
From letstalkscience.ca
Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science How Leverage Works Physics The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. A lever is a force. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. You cannot pull any out of thin. Web a lever works. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.thoughtco.com
The Physics Behind How a Lever Works How Leverage Works Physics The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n. How Leverage Works Physics.
From lessoncampussquiffy.z21.web.core.windows.net
Real Life Examples Of Lever How Leverage Works Physics Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. This. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.youtube.com
Levers as Force Multipliers and Gears GCSE Physics Revision YouTube How Leverage Works Physics Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance. The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. A lever is a force. This browser doesn't support html5.. How Leverage Works Physics.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Leverage Works Physics A lever is a force. This browser doesn't support html5. Web d2n2 −d1n1 = 0 d 2 n 2 − d 1 n 1 = 0. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance. A beam is placed on a. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.dreamstime.com
Classes of Lever Infographic Diagram for Physics Science Education How Leverage Works Physics The relative positions of the fulcrum and the load are adjusted to minimize the applied force. The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. You cannot pull any out of thin. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.dreamstime.com
Diagram of a simple lever stock vector. Illustration of machine 51314413 How Leverage Works Physics A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. A lever is a force. You cannot pull any out of thin. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. Web d2n2. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.dreamstime.com
Physics Leverage Explained by Mass and Distance Equation Stock Vector How Leverage Works Physics You cannot pull any out of thin. The beam pivots around the fulcrum and lifts the object. This browser doesn't support html5. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web a lever works by reducing the force applied to move a heavy object. Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the. How Leverage Works Physics.
From letstalkscience.ca
Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science How Leverage Works Physics The magnitudes of the two torques about the pivot point are equal, a condition known as the lever law. Web discover how the lever principle can multiply forces. A beam is placed on a fulcrum, and an object is positioned on the beam. In physics, work(energy) is conserved. You cannot pull any out of thin. Web levers are all around. How Leverage Works Physics.
From www.dreamstime.com
Physics leverage stock illustration. Illustration of archimedes 62357401 How Leverage Works Physics Web levers are all around us and within us, as the basic physical principles of the lever are what allow our tendons and muscles to move our limbs. This browser doesn't support html5. A lever is a force. A force is applied somewhere on the beam. Web in physics, work is defined as force times distance. In physics, work(energy) is. How Leverage Works Physics.